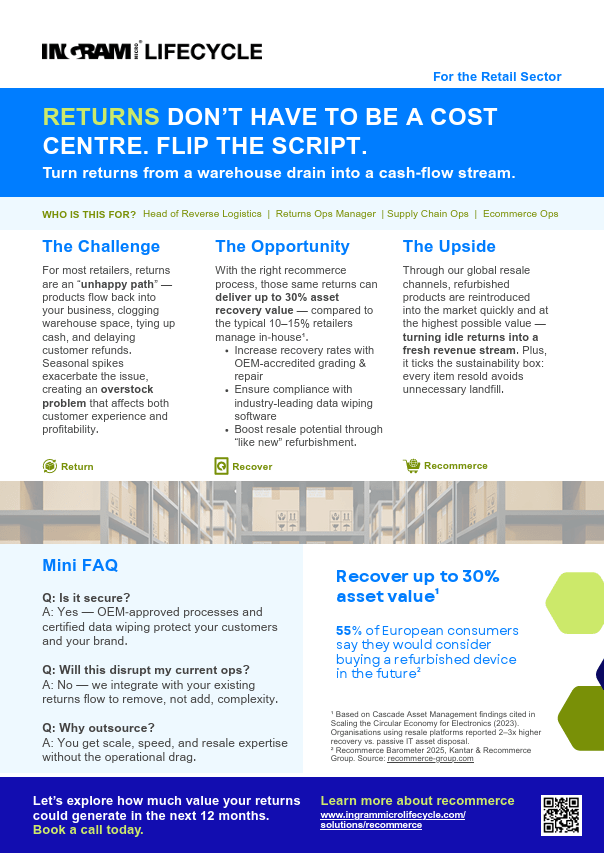
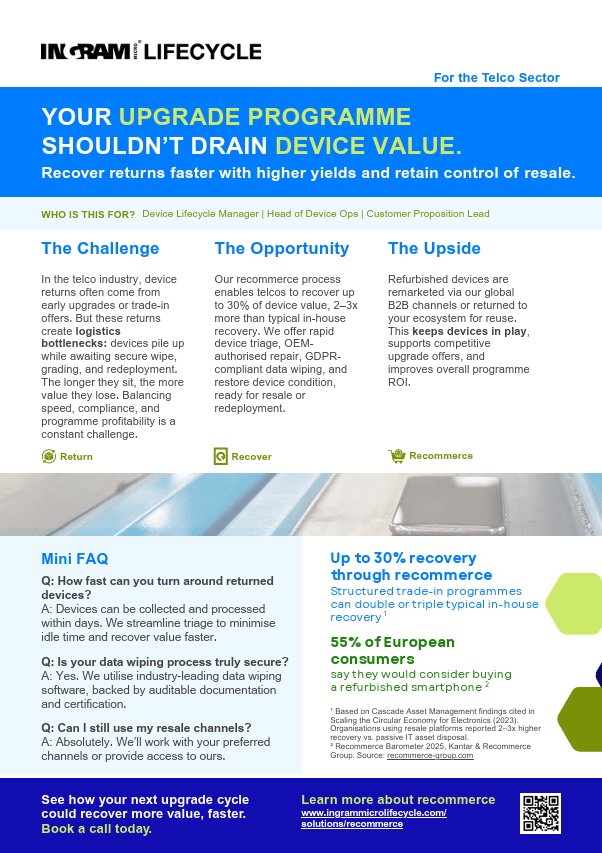
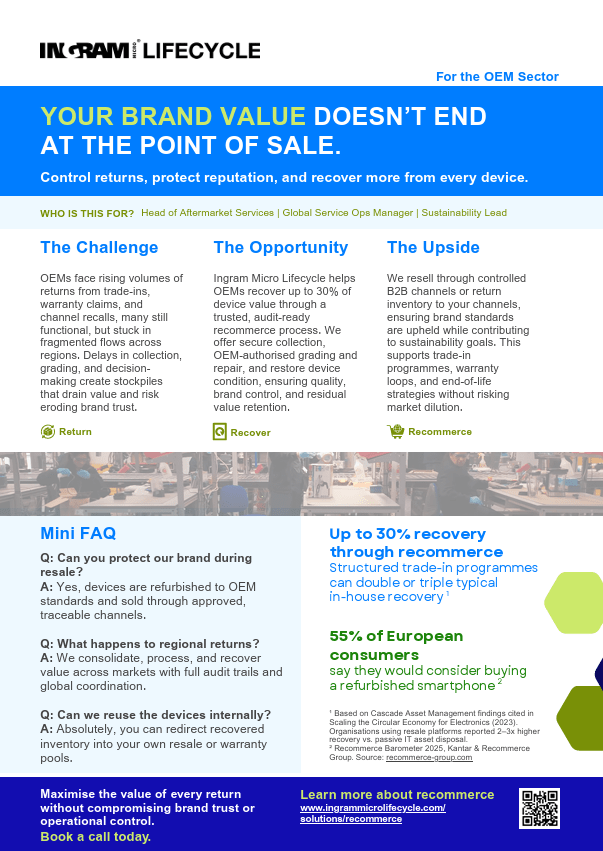
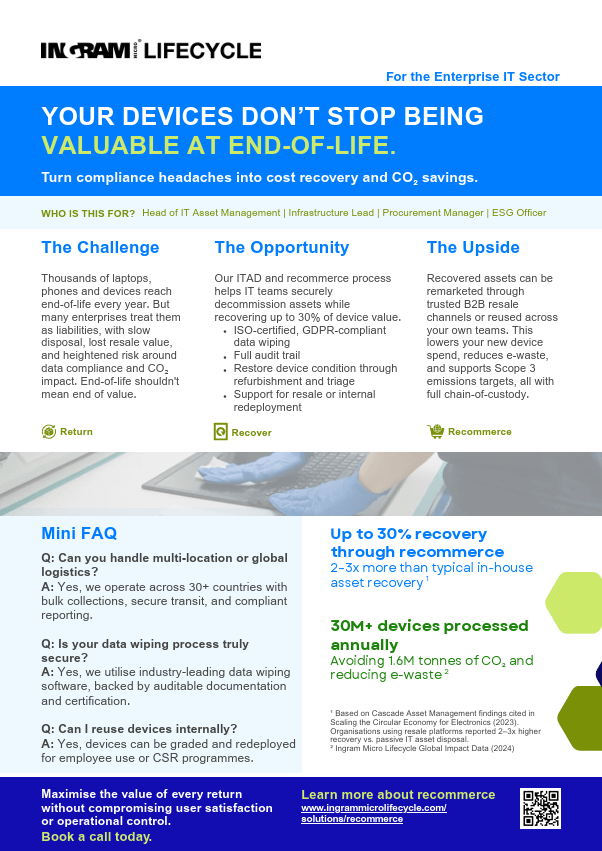
Recommerce
Ingram Micro Lifecycle provides comprehensive recommerce and remarketing services that include secure data wiping, cosmetic uplift, and value recovery of returned devices to prepare them for resale. These products are then returned to original channels or distributed through trusted B2B dealer networks across the UK, Europe, and the US.
Watch Dave Kempton, Director - Recommerce, in conversation with Paul Denham of ResearchHQ, as they demystify recommerce for retailers, OEMs, insurers, and enterprises handling electronic products.
Understanding recommerce
Recommerce, also known as reverse commerce or aftermarket sales, involves the process of selling previously owned, used products. Unlike traditional commerce, recommerce focuses on extending the lifecycle of items by repairing and refurbishing, then reselling and reusing them. This business model aligns with the principles of a circular economy, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Recommerce encompasses various transaction types, including business-to-business (B2B) buyback schemes, business-to-consumer (B2C) sales of refurbished goods, and consumer-to-business (C2B) trade-in programs. By facilitating the movement of products through these channels, recommerce helps reduce the environmental impact and offers financial benefits to both businesses and consumers.
Recommerce vs e-commerce: key differences
While both recommerce and e-commerce involve the sale of goods, they cater to different market needs and operate under distinct principles. E-commerce primarily deals with the sale of brand-new products, focusing on the linear economy's take-make-dispose model. In contrast, recommerce emphasizes the resale of used or refurbished products, promoting a circular economy by extending product lifecycles and reducing waste.
One of the critical differences between the two lies in their target markets. E-commerce attracts consumers seeking the latest products with the assurance of newness and warranty. Recommerce, on the other hand, appeals to cost-conscious and environmentally aware consumers who prioritize sustainability and affordability. This means that recommerce doesn’t cannibalize new product sales. By integrating recommerce into their business models, companies can tap into a broader audience and meet the growing demand for eco-friendly and budget-friendly options.
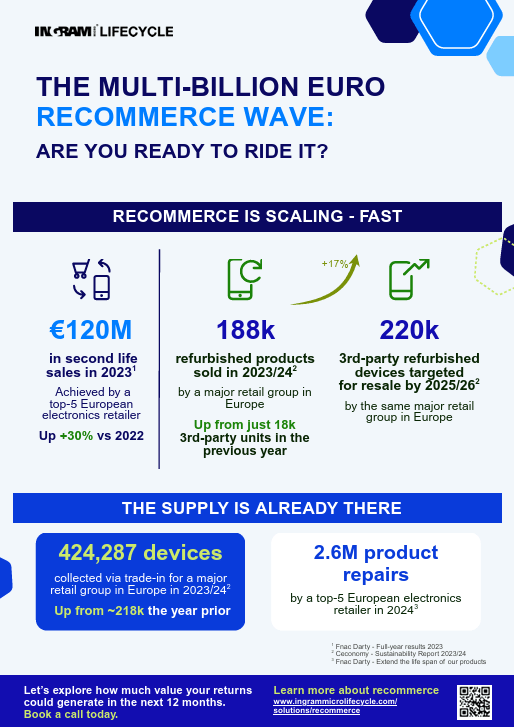
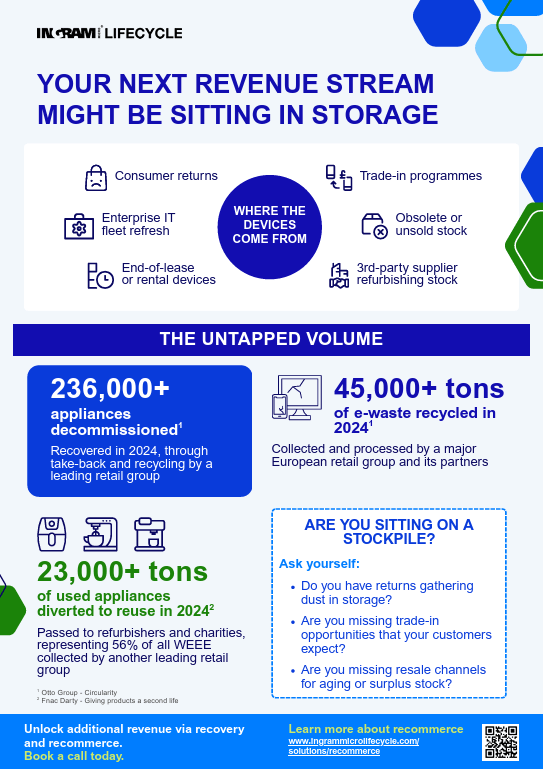
Download our latest infographics full of recommerce-focused industry insights.
The benefits of recommerce for modern businesses
Integrating recommerce into your business strategy offers numerous advantages, ranging from financial gains to enhanced sustainability credentials. Here are some of the key benefits.
Additional revenue stream: Recommerce provides businesses with an opportunity to monetize returned or unused products. By refurbishing and reselling these items, companies can create new revenue streams and reduce the financial impact of returns.
Reduced e-waste: By extending the lifecycle of products, recommerce helps mitigate the environmental impact associated with electronic waste. This approach not only conserves resources but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
Increased affordability: Recommerce makes technology more accessible to a wider audience by offering refurbished products at a fraction of the cost of new ones. This affordability can attract new customers and foster brand loyalty.
Enhanced brand reputation: Companies that adopt recommerce practices demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which can enhance their brand image and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Market expansion: By catering to the growing demand for refurbished products, businesses can expand their market reach and tap into new customer segments that prioritize cost and sustainability over brand-new items.
Addressing the challenges of recommerce
Despite its numerous benefits, recommerce presents several challenges that businesses must navigate to achieve success. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for building an efficient and profitable recommerce network:
Depreciation: The value of used products can depreciate quickly, especially if newer models are released. To mitigate this, businesses must streamline their recommerce processes to minimize the time products spend in storage.
Quality control: Ensuring the quality and functionality of refurbished products is essential for maintaining customer trust. Implementing rigorous testing, grading, and refurbishment processes can help achieve this.
Logistics: Efficient reverse logistics are vital for recommerce success. Companies must develop robust processes for collecting, transporting, and processing returned products to ensure timely resale.
Market demand: Understanding market demand is crucial for successful recommerce. Businesses must stay informed about consumer preferences and trends to align their inventory with market needs.
Partner selection: Choosing the right partners for refurbishment, repair, and resale is critical. Businesses should seek partners with the necessary expertise, resources, and capabilities to support their recommerce operations.
Ingram Micro Lifecycle's recommerce solution
Within Ingram Micro Lifecycle, our core service offering is built around three strategic pillars: return, recover, and recommerce. These principles guide our end-to-end approach to device lifecycle management, from initial intake through to resale or redeployment. Ingram Micro Lifecycle processes several million devices annually on behalf of leading OEMs and network carriers, with strong capabilities in OEM-approved, in-warranty repairs.
Our operations have evolved significantly in recent years, with a growing focus on cosmetic restoration and full refurbishment, transforming used products into high-quality, ready-for-market assets. These refurbished devices are then redistributed either back to the original provider or through an expansive B2B dealer network. With recommerce markets rapidly expanding across the UK, Europe, and the US, Ingram Micro Lifecycle’s recommerce efforts are now feeding growing demand in both direct and secondary channels.
While smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearables remain core categories, we’re increasingly extending services to a broader range of product types, including gaming consoles, VR headsets, drones, and small domestic appliances. The rise of subscription-based ownership models across these categories introduces new complexities for retailers, OEMs, insurers, and operators, particularly around logistics and product handling. Higher value and more fragile items present unique challenges in terms of cost, transport, and refurbishment standards. Ingram Micro Lifecycle’s expertise in this space enables our partners to navigate these complexities while unlocking greater value from their reverse logistics strategies.
Industry insight papers
Click to view and save our recommerce insight papers, tailored to individual industries, to see the challenges and opportunities that integration can present.